Skin Cancer Treatment in Bangalore
Skin cancers arise due to rapid multiplication and abnormal growth of skin cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, globally accounting for at least 40% of cancer cases. These lesions are malignant and harmful. Hence early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
Risk factors for Skin Cancer
- Ultraviolet light exposure from sun
- Fair skin
- Tobacco smoking
- Immunosuppression due to HIV/ AIDS infection or cancer or chemotherapy
- Exposure to X- Rays or chemicals like arsenic
- Certain types of sexually acquired wart virus infections
- Family or genetic predilection
- Elderly patients
Clinical features
Basal-cell carcinoma
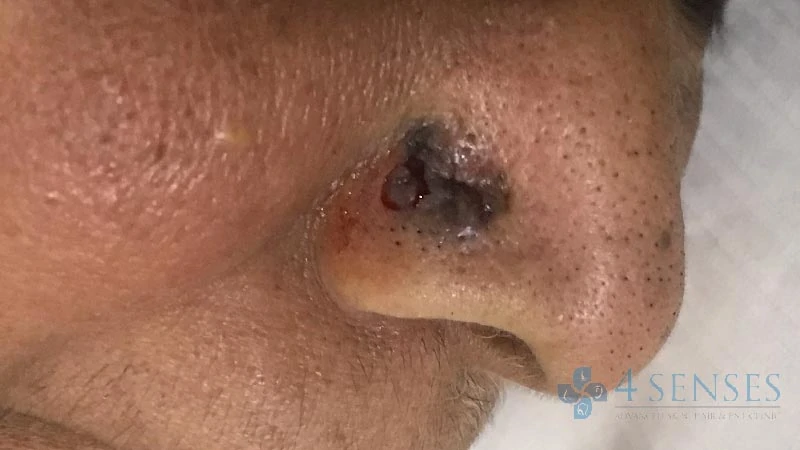
Basal-cell cancer is the most common type of skin cancer. It presents as a raised, smooth, pearly and waxy bump on the sun-exposed skin of the head & neck. It can also present with a grey - black pigmentation or lesions similar to psoriasis oand eczema. Small blood vessels can be seen within the tumor. The lesion may be asymptomatic or itchy and bleeds on touching. It develops crusting or ulcer at the center and hence it is also called as Rodent ulcer.
Squamous-cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell cancer (SCC) is second most common skin cancer. It appears as a pink - red colored elevated nodule or patch on sun-exposed skin. Lesions are friable and bleed and ulcerate easily. When SCC is not treated, it may develop into a large mass and gets fixed to underlying structures.
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant melanoma presents in different forms. These are the most aggressive of all skin tumors. Hence they require early intervention and treatment. Some lesions appear as brown to black patches on the palms and soles of hands and feet and even on the nails. Few melanomas present as nodules which grows rapidly and ulcerates or crusts. Some melanomas in elderly present on the sun damaged areas of face presenting as a small patch of about 1cm with irregular borders. Warning signs of malignant melanoma include change in the size, shape, color or elevation of a mole.
Management
The condition is diagnosed by physical examination and confirmed by skin biopsy and histopathological examination.
- Surgical removal done for smaller lesions by curettage, electrosurgery, cryotherapy or surgical excision of the lesion.
- Mohs surgery - This procedure is for larger, recurring or difficult-to-treat skin cancers. And for the lesions over lips, eyelids, nasal tips, genitalia etc where the underlying organ needs to be preserved.
- Radiotherapy - High-powered energy beams, such as X-rays, to kill cancer cells. This is an option when cancer can't be completely removed during surgery.
- Chemotherapy - Drugs are used to kill cancer cells. For cancers limited to the top layer of skin, creams or lotions containing anti-cancer agents may be applied directly to the skin or injected intralesionally.
- LASERS - CO2 , Nd:YAG and PDL lasers have been used to ablate the lesion.
Treatment for Skin Cancer at 4 Senses Clinic, Bangalore
Doctors at 4 Senses Clinic take history patiently, examine the patient thoroughly and diagnose the condition with minimal and necessary investigations. After finding out the root cause of problem, they provide accurate treatment. The doctors also counsel on how to prevent further recurrences. If you are looking at the treatment for skin cancer, contact Call:6366494494
