Bacterial Infection treatment in Bangalore
Skin functions as a barrier by preventing the entry of numerous disease causing microorganisms. Cuts or injuries or certain skin diseases cause a breech in the continuity of skin thus providing a way for the entry of pathogens from outside environment into the body. This leads to infections.Bacterial skin infections are common, ranging in severity from mild to life-threatening.
Causative organisms
The organisms which cause infections are numerous. Most of the infections are caused by staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus organisms . Other bacteria which can cause infection are corynebacterium species, Mycobacterium tuberculosis , gram negative bacterias like klebshiella, enterobacter, pseudomonas species etc.
Risk factors
Bacterial skin infections develop when bacteria enter through hair follicles or through small breaks in the skin that result from scratches, punctures, surgery, burns, sunburn, animal or insect bites, wounds, and pre-existing skin disorders.
Though anybody can develop the infection, some people are at more risk:
- People with diabetes, who are likely to have poor blood flow (especially to the hands and feet) and poor immunity.
- People who are elderly with other co morbidities conditions.
- People who do not maintain good hygiene.
- People who have human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), AIDS or other immune disorders, or hepatitis etc
- People who are undergoing chemotherapy or treatment with other drugs that suppress the immune system
- People who have an inflamed or damaged skin are more likely to become infected. Any break in the skin predisposes a person to infection.
Common Bacterial Skin Infections
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection affecting the deeper layers of the skin: the dermis and the subcutaneous tissue. Cellulitis is associated with both Staphylococcus and Streptococcus although many other types of bacteria can cause the condition.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is a bacterial infection that occurs in the top two layers of skin. It can be very painful and cause an intense, burning sensation. Erysipelas is similar to cellulitis but affects different skin layers.
Folliculitis
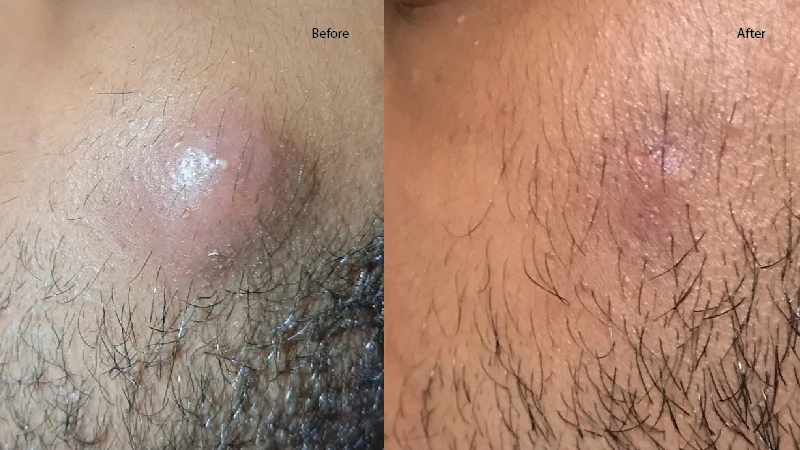
Folliculitis is an infection of a hair follicle. It looks like a tiny red or white pimple at the base of a hair. There may be only one infected follicle or many. Each infected follicle is itchy or slightly painful.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection of the top layer of skin called the epidermis. It is highly contagious and more commonly seen in children than adults. The organisms usually occur around the nose and mouth but can be spread to other parts of the body through skin-to-skin contact, clothing.
Boils or Furuncles
Boils are deep skin infections that start in hair follicles and later spread to the tissue around the hair follicle. Boils are firm, red, tender bumps that progress until pus accumulates underneath the skin. Furuncles are common on the neck, breasts, face, and buttocks. They are uncomfortable and may be painful when closely attached to underlying structures.
Abscess
Skin abscesses are warm, painful, pus-filled pockets of infection below the skin surface that may occur on any body surface. Abscesses may be one to several inches in diameter. Abscess are severely painful and needs to be drained by incision.
Erythrasma
Erythrasma is an infection of the top layers of the skin caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium minutissimum. Erythrasma affects mostly adults, especially those with diabetes. Erythrasma is most common in the foot, groin, armpits, skin folds under the breasts or on the abdomen, and the area between the vaginal opening and the anus.
Tuberculosis of skin
In India tuberculosis continues to be the biggest public health problem and cutaneous tuberculosis is not so uncommon. The disease presents with a wide variety of morphological features with variable duration of the disease. Once the condition is suspected by clinical examination, the diagnosis is confirmed by skin biopsy & histopathological examination.
Treatment
Main stay of treatment is antibiotic.
1.Whether to treat with topical antibiotics or systemic, depends on
- Depth and extent of the infection
- Presence of complications/ risk factors
- Systemic involvement
- Underlying immunosuppressed state.
2.The class of antibiotic depends on the type of causative organism, culture and sensitivity and resistant strain of organism, condition of the patient.
3.If there is an abscess, then it needs to be drained.
4.If the causative organism is Mycobacterium tuberculosois, then Antitubercular medications are to be started.
5.Occasionally, infections like erysipelas and cellulitis may necessitate hospitalization if signs of rapid progression develop.
6.Underlying co morbid condition needs to be identified and treated to prevent recurrences of condition.
Doctors at 4 Senses Clinic take history patiently, examine the patient thoroughly and diagnose the condition with minimal and necessary investigations. After finding out the root cause of problem, they provide accurate treatment. The doctors also counsel on how to prevent further recurrences. If you are looking at treatment for Bacterial infection, contact Call:6366494494
