Fungal Infections of Scalp Treatment in Bangalore
Tinea capitis is the name used for infection of the scalp and hair with fungus. Common in children between 3 to 12 years and tinea capitis is less frequently seen in adults.
Causitive organism - caused by various dermatophytes (fungi) most commonly by Trichophyton and microsporum species.
Transmission of Fungal infections on scalp
Tinea capitis is a communicable infection transmitted from person to person by intimate personal contact, via fallen infected hair, shared hair brush, combs and hats.
Symptoms of Fungal infections on scalp
Fungal infection on scalp can present with any of the following features. Classified into Inflammatory and Non inflammatory types.
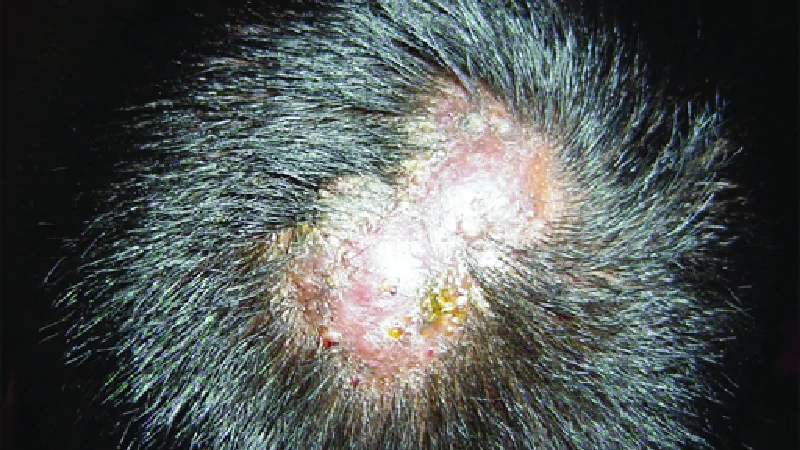
Inflammatory types :
- Kerion - Inflammed , tender, boggy swelling with tiny pus filled areas on scalp.
- Flavus - Yellow cup shaped crust with matted hair & musty odor on scalp.
Non inflammatory types :
- Gray patch - Patches of partial hair loss , circular in shape with numerous broken off hair and dandruff like scales.
- Black dot - Hair shaft is extremely brittle and breaks off at the level of scalp. The remnant of hair left behind appears as black dot on examination.
- Carrier state — no symptoms and only mild scaling
Tinea capitis may result in swollen lymph glands at the sides or the back of the neck. Untreated kerion and favus may result in permanent scarring and bald areas.
Diagnosis
We suspect Tinea capitis if there is a combination of scale and bald patches. Wood light fluorescence is helpful in diagnosing. The diagnosis of tinea capitis is confirmed by microscopy and culture of skin scrapings and hair pulled out by the roots. Sometimes skin biopsy may be required for histopathological examination. At 4 senses we have all diagnostic test modalities to identify the cases of tinea capitis in initial stage itself. So with early diagnosis and early treatment, the disease progression can be stopped and many other complications of the disease can be avoided.
Treatment for Fungal infections on scalp
- Tinea capitis is usually treated with topical and oral antifungal medicines according to the severity of the condition .
- If there is a secondary infection, it needs to be corrected with antibiotics.
- Oral corticosteroids in markedly inflammed conditions to reduce the incidence of scarring.
- Removal of matted crusts and repeated medicated shampooing.
- In cases of untreated and neglected Tinea capitis, where bald patch has already developed , hair transplantation will help in restoring hair there once the infection is completely cured.
Doctor's in 4 Senses Clinic will properly diagnose the root cause of the problem and treat the same accordingly with an aim to cure the disease. For Doctor’s Appointment Contact Call:6366494494
